Generative AI: the New Gold Rush in Tech Industry
In an era where technology has become deeply interwoven with our daily lives, artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly advancing and transforming the world in unprecedented ways. One key development in the AI landscape is the rise of generative AI, a technology capable of creating content that is often indistinguishable from that made by humans. From generating realistic text to designing artwork and even composing music, generative AI is a powerful tool with limitless potential. However, with these advancements come various implications and challenges. This article seeks to explore the intricate workings of generative AI, its myriad applications across different industries, its potential impact on employment, and the critical ethical considerations that need to be addressed as we move towards an increasingly AI-driven future.
The Emergence of Generative AI
Over the last decade, AI has made significant strides, leading to breakthrough innovations in several industries. In this dynamic AI landscape, Generative AI has emerged as an exciting and transformative technology. Generative AI algorithms, including notable ones like OpenAI's ChatGPT, have been making headlines for their ability to create new content, ranging from text, audio, images, to videos, and even complex simulations.
The term 'Generative AI' is often used to describe these advanced AI systems capable of generating new data that closely resemble the original input data. Instead of merely predicting or classifying, these algorithms can construct, improvise, and innovate, behaving in a way that mirrors human creativity. The secret to their success lies in their unique machine learning capabilities. These AI systems are trained on massive datasets, enabling them to recognize patterns, learn from them, and subsequently generate new data that maintain the consistency and context of the original input.
Generative AI is not just an exciting technological phenomenon; it's a game-changer that is poised to revolutionize the way we create and consume content. It's the driving force behind some of the most captivating advancements in tech, from realistic deepfake videos to AI-generated art and music. The tech industry is increasingly seeing the applications of Generative AI in content creation, design prototyping, and even in areas such as creating virtual worlds for video games.
The rise of generative AI is akin to a new gold rush in the tech industry. Its potential to significantly impact how we live and work is drawing interest and investment from major tech players, startups, and individual developers alike. However, as with any groundbreaking technology, it also brings with it a unique set of challenges, opportunities, and ethical considerations that we must understand and navigate carefully.
The Underlying Technology and Principles of Generative AI
At the heart of generative AI lies a specialized form of machine learning known as deep learning, specifically a subtype called Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). Proposed by Ian Goodfellow in 2014, GANs are composed of two neural networks - a Generator and a Discriminator - that work together in a competitive scenario. The generator network's role is to create new data, while the discriminator's task is to evaluate this data's authenticity compared to the original training set.
GANs operate using a unique adversarial process, reminiscent of a counterfeiter and a police officer. The generator network (counterfeiter) aims to produce data so authentic that the discriminator network (police) cannot distinguish it from the original data set. Simultaneously, the discriminator strives to improve its ability to catch the generator's 'fakes'. This back-and-forth game continues until the generator becomes adept at creating data indistinguishable from the real dataset, leading to impressive generative results.
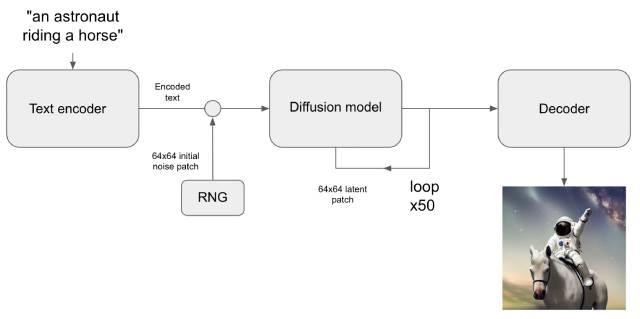
Alongside GANs, another essential tool in generative AI is the Transformer architecture, most notably used in natural language processing (NLP). Transformers, such as OpenAI's GPT series, create coherent and contextually relevant text by using attention mechanisms to understand the relationships and dependencies between words in a sentence, and even across multiple sentences. These models are trained on extensive corpora of text, enabling them to generate human-like responses, translate languages, summarize text, and much more.
Despite their powerful capabilities, generative AI models have limitations. They require extensive computational resources for training, and their black-box nature makes it challenging to understand their decision-making process. Furthermore, their ability to generate incredibly realistic synthetic data raises significant ethical and legal questions that society is only beginning to grapple with.
Applications of Generative AI
Generative AI has an array of practical applications across various industries, from entertainment and art to science and healthcare. In the art and entertainment sector, it can be used to generate music, create unique digital artwork, and develop characters for video games. These applications allow creators to generate new content quickly, providing a unique avenue for creativity and innovation.
In the field of healthcare, generative AI has shown potential in drug discovery and molecular design. AI models can generate potential drug molecules, test their effectiveness in silico, and predict side effects, speeding up the lengthy and costly drug discovery process. Additionally, generative AI can create synthetic medical datasets, allowing researchers to train other AI models without risking patient privacy.
Generative AI is also being harnessed in the business domain for tasks like content generation and product design. For example, AI can generate product descriptions, advertisements, and even news articles, saving time and resources. Similarly, generative design tools can produce numerous design variations based on specific criteria, helping engineers and architects optimize their designs.
Nevertheless, while generative AI presents significant opportunities, it also poses new challenges and risks. The ability to generate realistic synthetic data has implications for disinformation and deepfakes, creating potential for misuse. Ensuring the responsible use of these powerful tools is thus of utmost importance.
Generative AI and Ethical Considerations
The rapid advancements in generative AI have sparked a vibrant discussion about its ethical implications. One significant concern pertains to deepfakes—highly realistic images, audio, and video generated by AI that are virtually indistinguishable from real ones. These can be misused to spread disinformation, manipulate public opinion, or defame individuals, raising questions about authenticity and trust in the digital world.
In addition, the potential for job displacement is a key concern. As generative AI becomes more capable of performing tasks such as content creation and design, the fear that it might replace human jobs in these areas grows. However, optimists argue that AI will rather take over repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for more creative and strategic tasks.
Another major ethical issue is data privacy. Generative AI models, especially those that are trained on large datasets, can inadvertently leak information about the data they were trained on, potentially compromising privacy. Thus, ensuring that data used to train these models is handled responsibly and securely is paramount.
Finally, it's essential to consider accountability in AI-generated outcomes. When AI creates something new, who owns it? Who is responsible if the AI generates harmful or illegal content? These are complex questions that require thoughtful regulation and governance. As generative AI continues to evolve, ethical considerations and guidelines will play a crucial role in shaping its future.
Conclusion
As we continue to advance into a future shaped by artificial intelligence, generative AI has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with technology, making it an even more integral part of our lives. From fostering creativity to enhancing productivity and driving industry growth, the possibilities are boundless. However, alongside these promising benefits, we must also navigate a complex landscape of challenges - ensuring ethical and responsible use, addressing potential biases, and making sure that this powerful technology is used in a way that benefits all sectors of society.
In conclusion, generative AI isn't just about machines creating content - it's about unlocking a new dimension of human potential and reshaping the future of work, creativity, and innovation. By understanding this transformative technology, its benefits, and its challenges, we can ensure we are well-equipped to leverage its potential and responsibly navigate the road ahead. Let's embrace the creative genius of generative AI, while maintaining a strong ethical compass, and together, we can navigate towards a future where AI and human intelligence harmoniously coexist.
LEAVE A REPLY
Your email address will not be published.
Stay up to date with the latest news from the technology, software and business sector!
Subscribe to our newsletter!
